UK researchers have studied the arrangement between the devout settlement and the death threat from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in England and Wales. retrospective investigation of the variation in the threat before and after the closure of the devoted organization in England and Wales,” published on the medRxiv online pre-publication page.
Researchers led by Charlotte Hannah Gaughan of the Office of National Statistics, Newport, UK, write that there are several socioeconomic and behavioral points related to the COVID-19 death threat caused by SARS CoV2. Some of these points have been linked to blockades that have prevented others from meeting. They wrote that “devotee meetings have been linked to the spread of COVID” and attempted to perceive diversifications in the threat of COVID-19-related deaths among devoted teams in the UK before and after lockdowns.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has expressed its fear that devout practices and meetings may “contribute to the spread of COVID 19”. The authors write that the threat of transmission is accumulating with “networks of devout prayers and maximum participation in devout meetings and festivals “that increase the chances of transmission of the network. The authors write: “Several studies have shown that epidemics around the world have been attributed to centers of worship and devout ceremonies. “
In the United Kingdom, the law required banning devout meetings on 23 March 2020 to prevent the spread of COVID-1 on the network. Wales before and after such blocking measures.
The authors write that approximately 67 percent of the British population identifies with a religion that does not participate in a devout practice. They noted that “75% of Sikhs attend normal practices, while only 29% of Christians do.
The team used the 2011 Census of England and Wales and death records to look for the age-adjusted threat of dying with COVID 19 for the devoted group. They also collected sociodemographic data on deaths and occupational exposure threats to the disease.
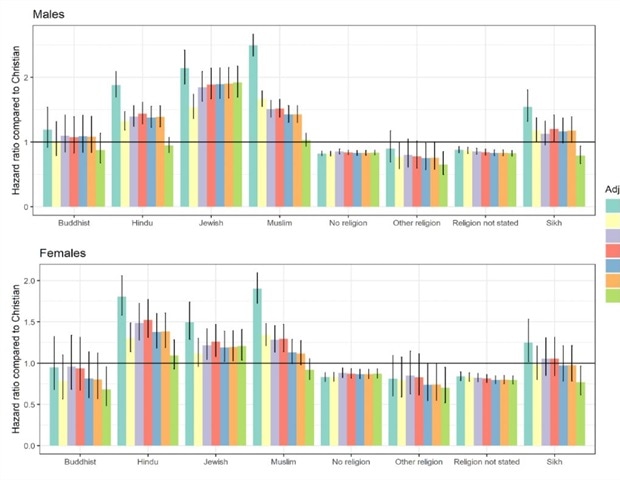
This is a retrospective cohort test of 48,422,583 others from the 2011 census. The death certificate has been used to detect the death threat in individuals. To evaluate the arrangement between the two, they used Cox regression models. ) before and after the lockout period. There were a total of 36,726 COVID deaths, they noted. In total, nine devoted teams were identified: “Without faith, Christian, Buddhist, Hindu, Jewish, Muslim, Sikh, no other faith or faith not indicated. “Follow-up from 2 March 2020 to 15 May 2020.
The effects of the review showed a different arrangement between the arrangement and the COVID-19 mortality threat. The general effects were:
Investigators concluded that “Jews remained at a greater death threat (due to COVID-19) for all other groups. “They wrote, “Blocking measures were linked to relief from differences in COVID 19 mortality rates among devoted groups” and called for more studies to read about the effectiveness of banning devout meetings to reduce the threat of COVID-19-related deaths.
medRxiv publishes initial clinical reports that are not peer-reviewed and therefore should not be considered conclusive, the consultant’s clinical practice/health-related habit or treated as established information.
Written by
Dr. Ananya Mandal is a doctor by profession, a teacher by vocation and a doctor out of passion. He specialized in clinical pharmacology after his bachelor’s degree (MBBS). For her, fitness communication isn’t just about writing complex critiques for professionals, it’s about making medical wisdom understandable and available to the general public.
Use one of the following to cite this article in your essay, job, or report:
Apa
Mandal, Ananya. (2020, 07 October). Religion and COVID-19 in the United Kingdom. News-Medical. Recovered October 7, 2020 at https://www. news-medical. net/news/20201007/Religion-and–of-COVID-19-in-UK . aspx.
Mla
Mandal, Ananya. ” Religion and COVID-19 in the United Kingdom. “News-Medical. 07 October 2020.
Chicago
Mandal, Ananya. ” Religion and COVID-19 in the United Kingdom. “News-Medical. https: //www. news-medical. net/news/20201007/Religion-and–of-COVID-19-in-UK. aspx. (accessed 7 October 2020).
Harvard
Mandal, Ananya. 2020. Religion and COVID-19 in the United Kingdom. News-Medical, accessed 07 October 2020, https://www. news-medical. net/news/20201007/Religion-and–of-COVID- 19 at UK. aspx.
News-Medical. net – An AZoNetwork site
Ownership and operation through AZoNetwork, © 2000-2020